Computed Tomography Ct Sinuses
Detailed information on sinusitis, including causes, symptoms, penaksiran, and treatment. due to interest in the covid-19 vaccines, we are experiencing an extremely high call volume. please understand that our phone lines must be clear for u. Acute sinusitis. dr francis deng and assoc prof frank gaillard et al. acute sinusitis (rare plural: sinusitides) is an acute inflammation of the paranasal sinus mucosa that lasts less than four weeks and can occur in any of the paranasal sinuses. if the nasal cavity mucosa is also involved then the term rhinosinusitis may be used. A ct scan is one of the safest means of studying the sinuses. ct is the most reliable imaging technique for determining if the sinuses are obstructed. it is the best imaging modality for sinusitis. ct of the sinuses can help plan the safest and most effective surgery. Functional endoscopic sinus surgery (fess) has revolutionised the approach and treatment of chronic rhinosinusitis. certain anatomical variations are thought to be predisposing factors for the development of sinus disease and it is necessary for the surgeon to be aware of these variations, especially if the patient is a candidate for fess 10.
Chronic sinusitis is defined clinically as a sinonasal infection lasting more than 12 weeks. patients may present with symptoms of sinusitis such as nasal obstruction, nasal discharge, facial pain, headache, halitosis, anosmia, etc. Imaging findings are nonspecific and can be seen in a large number of asymptomatic patients (up to 40%) 11. imaging findings should be interpreted with clinical and/or endoscopic findings. a gas-fluid level is the most typical imaging finding. however, it is only present in 25-50% of patients with acute sinusitis 4. opacification of the sinuses and gas-fluid level best seen in the maxillary sinus. it does not allow assessment of the extent of the inflammation and its complications. the most common method of evaluation. better anatomical delineation and assessment of inflammation extension, causes, and complications. peripheral mucosal thickening, gas-fluid level in the paranasal sinuses, gas bubbles within the fluid and obstruction of the ostiomeatal complexesare recognized findings. rhinitis, often associated with sinusitis, is often characterized by thickening of the turbinates with obliteration of the surrounding air channels. this should not be confused with the normal nasal cyc A characteristic feature on ct sinuses is sclerotic thickened bone (hyperostosis) involving the sinus wall from a prolonged mucoperiosteal reaction. intrasinus calcificationmay be present. the presence of opacification is not sinusitis radiology a good discriminator from an acute sinus infection. there are five main patterns of chronic inflammatory disease that classify the disease into distinct anatomical/pathological groups and are dependent on the drainage pathways affected. this classification helps the surgeon to select the type of surgery needed 12: 1. ostiomeatal complex pattern: maxillary sinus, anterior ethmoid air cells, and frontal sinuses are affected due to obstruction of the ostiomeatal complex 2. infundibular pattern: isolated obstruction to the ethmoid infundibulum and/or maxillary sinus ostium 3. sphenoethmoidal recess pattern: inflammatory changes in the sphenoethmoidal recess obstruct the sphenoid sinus in isolation or in conjunction with the posterior ethmoidal air cells 4. sinonasa
Symptoms Of Sinusitis Facty Health
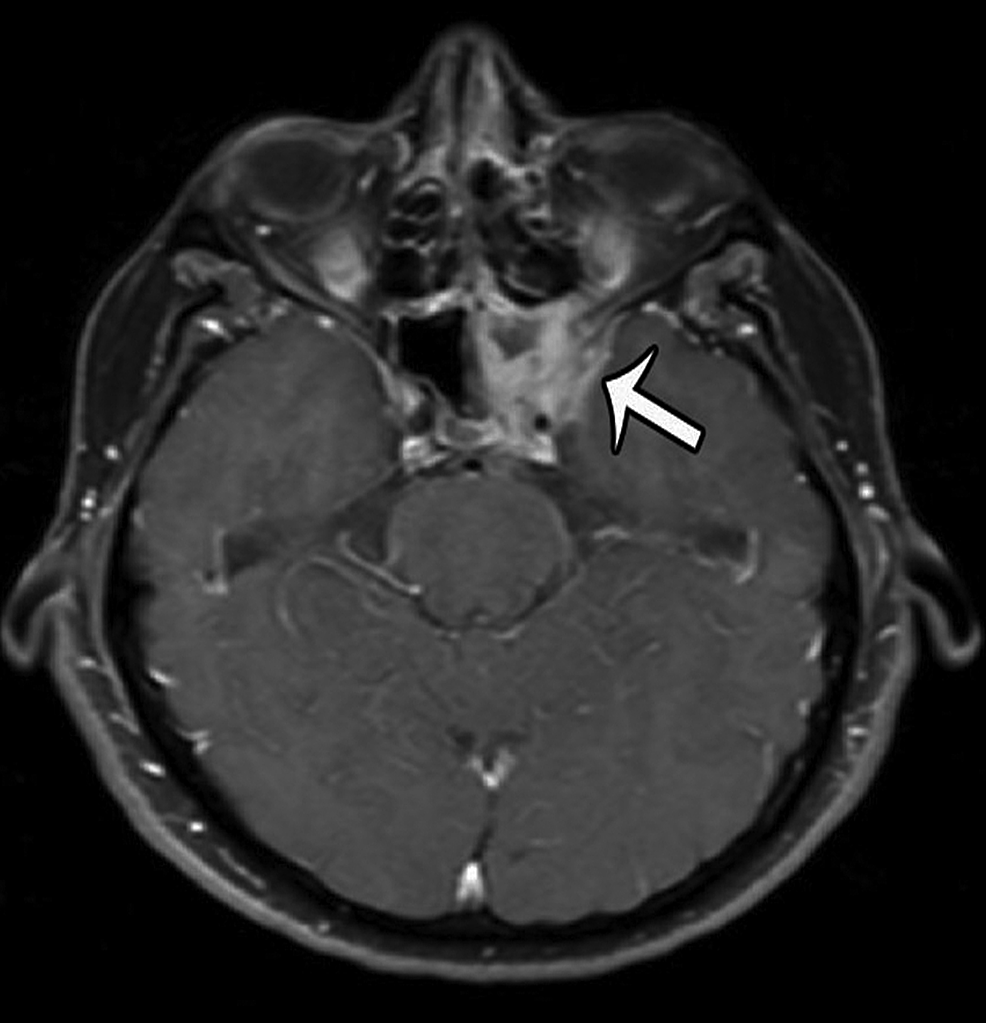
Sinusitis is a broad and non-specific term referring to the inflammation within the paranasal sinuses. there are several forms which are specific entities based on etiology and clinical features, and hence covered individually: acute sinusitis. Sinusitis is caused by inflammation of the sinuses, which often develops due to bacteria stuck in the nasal passages. the condition is most common following a lengthy cold or the flu but can be caused by allergies, as well. symptoms of sinu.
Sinusitis is a clinical penaksiran that relies on the presence of signs and symptoms such as facial pain/pressure/fullness, mucopurulent nasal drainage, nasal congestion/obstruction, and reduction in sense of smell. to establish a penaksiran of chronic sinusitis, these symptoms should be present longer than 12 weeks despite attempts at medical management. dental pain in odontogenic sinusitis can occur but is often absent. sinusitis radiology patients who have imaging evidence of sinus mucosal inflammation are not necessarily symptomatic. Nov 15, 2002 · sinusitis is one of the most common diseases treated by primary care physicians. uncomplicated sinusitis does not require radiologic imagery. however, when symptoms are recurrent or refractory.

Introduction. paranasal sinusitis is a common clinical condition that affects approximately 16% of adults in the united states each year . the disease has adverse impacts on both the quality of life for afflicted patients, as well as a substantial socioeconomic burden due to costs associated with medical care, decreased productivity, and absences from work or school . See full list on radiopaedia. org. See full list on radiopaedia. org. Sinusitis is one of the most common diseases treated by primary care physicians. uncomplicated sinusitis does not require radiologic imagery. however, when symptoms are recurrent or refractory.
Fungal sinusitis. dr bahman rasuli and assoc prof frank gaillard et al. fungal sinusitis is a collective term referring to a number of entities, which can be divided into two groups, depending on the presence of fungal hyphae within or beyond the mucosa 1: non-invasive: hyphae do not invade the mucosa. allergic fungal sinusitis. Search radiology technology school. get results from 6 engines at once. Sinusitis is a complaint many people experience even if they don't immediately recognize the medical term. sinusitis is an inflammation of sinuses, or to be a little more exactly, of their linings. sinusitis radiology in most cases the cause is viral, and it i.
Allergic fungal sinusitis accounts for 5-10% of chronic hypertrophic sinus disease going to surgery. it is seen in young immunocompetent patients (mean age range 23-42 years). in children, m:f ratio = dua:1 and in adults, m:f ratio = 1:1. 4. The most common finding that supports, but does not establish, a diagnosis of odontogenic sinusitis is mucosal thickening in the inferior maxillary sinus (>2 mm is abnormal, >10 mm is marked/severe). unilateral and isolated maxillary sinus opacification should raise the possibility of an odontogenic cause. multiplanar evaluation of the maxillary molars and premolars and surrounding bone should be undertaken to identify a source, such as periapical lucency, periodontal bone loss, oroantral fistula, and exogenous dental reconstructive/restorative material. Chronic sinusitis is defined clinically as a sinonasal infection lasting more than 12 weeks. patients may present with symptoms of sinusitis such as nasal obstruction, nasal discharge, facial pain, headache, halitosis, anosmia, etc. it is worth noting is no definite correlation between symptoms and imaging findings of chronic sinusitis and that endoscopic chronic sinusitis may have no imaging correlation as the mucosa is best appreciated on the former 11.
5 home remedies for sinusitis howstuffworks.
Posting Komentar untuk "Sinusitis Radiology"